The Power of Antioxidants
The Power of Antioxidants: Protecting Your Body from Oxidative Stress
In today’s world, our bodies are constantly exposed to environmental toxins, stress, and poor diet choices that can lead to the formation of harmful molecules known as free radicals. These free radicals can damage our cells, proteins, and DNA, contributing to aging, disease, and overall poor health. Fortunately, the body has its own defense mechanism against these dangerous molecules—antioxidants.
Antioxidants are naturally occurring compounds found in foods and produced by our bodies that neutralize free radicals, helping to protect our cells from oxidative stress and damage. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the role of antioxidants in the body, their health benefits, and the best sources of these powerful compounds.
What Are Free Radicals?
Free radicals are unstable molecules that contain unpaired electrons. To stabilize themselves, they steal electrons from other molecules in the body, a process called oxidation. While this is a normal part of cellular function, excess free radicals can overwhelm the body’s defenses and cause oxidative stress—a condition that damages cells and is linked to a variety of chronic diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s (Halliwell & Gutteridge, 2015).
The Role of Antioxidants
Antioxidants work by donating electrons to free radicals, neutralizing them and preventing them from causing harm to healthy cells. By protecting our cells from oxidative damage, antioxidants play a crucial role in:
Reducing Oxidative Stress
The primary function of antioxidants is to reduce oxidative stress, a condition where free radicals outnumber the body’s antioxidant defenses. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help prevent cellular damage that can contribute to chronic diseases and aging (Halliwell & Gutteridge, 2015).Enhancing Metabolic Detoxification
Many antioxidants, particularly those found in the liver, support the detoxification process by neutralizing free radicals generated during the breakdown of toxins. This helps the body eliminate harmful substances like environmental pollutants, medications, and metabolic waste products (Borras et al., 2010).Supporting the Immune System
Antioxidants play a vital role in supporting the immune system. Vitamins like vitamin C and E enhance the function of immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages, making the body more effective at fighting infections (Maggini et al., 2010).Reducing Chronic Disease Risk
Oxidative stress is a key contributor to the development of chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Antioxidants help reduce this risk by protecting tissues from oxidative damage and inflammation (Lobo et al., 2010).Fighting the Effects of Aging
One of the most well-known benefits of antioxidants is their role in slowing down the aging process. As we age, our bodies accumulate oxidative damage, which leads to the breakdown of cellular structures and functions. Antioxidants help mitigate these effects, promoting longevity and overall health (Finkel & Holbrook, 2000).
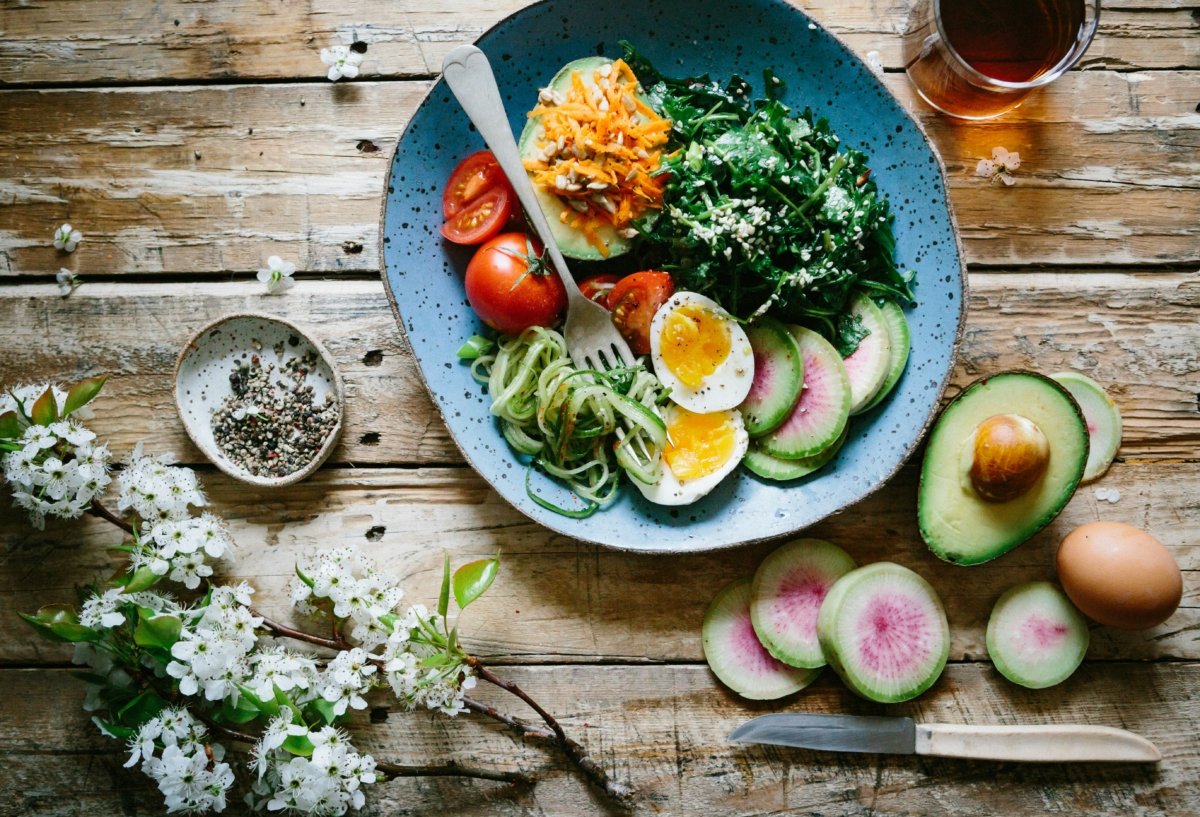
Top Sources of Antioxidants
The best way to ensure you’re getting enough antioxidants is through your diet. Many antioxidant-rich foods are also packed with other essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Here are some of the top sources:
Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are loaded with antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which give them their vibrant color.
Leafy Greens: Kale, spinach, and other dark, leafy greens are excellent sources of antioxidants like vitamins C and E.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds are rich in vitamin E, a potent antioxidant.
Green Tea: Green tea is a rich source of catechins, a type of antioxidant that has been shown to support heart health and reduce the risk of cancer.
Dark Chocolate: Yes, dark chocolate! It’s high in flavonoids, which are powerful antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Beans and Legumes: Beans like kidney beans and lentils are excellent plant-based sources of antioxidants, particularly polyphenols.
Conclusion
Antioxidants are an essential part of maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases. By neutralizing harmful free radicals, antioxidants protect your cells from oxidative damage, support metabolic detoxification, regulate the immune system, and even reduce the effects of aging. To get the most benefit, focus on incorporating a wide variety of antioxidant-rich foods into your diet.
Remember, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds will provide you with the best defense against oxidative stress and help keep your body healthy for years to come.
References:
Halliwell, B., & Gutteridge, J. M. C. (2015). Free radicals in biology and medicine (5th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Borras, C., et al. (2010). The role of antioxidants in the liver’s detoxification processes. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 48(4), 407-419. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.11.009
Maggini, S., et al. (2010). The role of vitamin C and other antioxidants in immune function. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 69(3), 363-370. doi:10.1017/S0029665110001766
Lobo, V., et al. (2010). Free radicals, antioxidants, and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacognosy Reviews, 4(8), 118-126. doi:10.4103/0973-7847.70902
Finkel, T., & Holbrook, N. J. (2000). Oxidants, oxidative stress, and the biology of aging. Nature, 408(6809), 239-247. doi:10.1038/35041687
Tags:
Recent posts
-

Why You Feel Hypothyroid Even When Your Labs Are “Normal”
02/21/2026 at 12:10
-

Thyroid Weight Gain: Why Dieting Stops Working
02/21/2026 at 09:02
-
GI Symptoms Explained: How to Relieve Digestive Issues with Nutrition
01/14/2026 at 14:57
-

Eating Healthy in the New Year: Mindful, Sustainable Habits That Actually Last
01/05/2026 at 14:19
-

Wellness and Nutrition for People Living With Autoimmune Diseases
11/11/2025 at 18:22
-

Nutrition Counseling: What does the first session entail?
10/23/2025 at 13:24
-

The Power of Nutrition in Perimenopause and Autoimmune Health
10/19/2025 at 19:45
-

How Nutrition Can Help Manage Chronic Pain: Evidence & Tips
10/16/2025 at 17:47


Leave a reply