It is estimated that 280 million worldwide suffer from depression (Depression, n.d.). People use the word depression very loosely, but depression is not simply a down moment in life or us facing the challenges of daily life. Clinical depression is much more severe than that. It is also known that depression can lead to suicide, and it is not treated depending on socioeconomic status and because of the stigma surrounding mental illness.
Studies indicate that a whole foods diet is protective against one of the most widespread disorders: depression. Depression is also correlated with inflammation. That makes sense if we start thinking that not all calories are not created equally. In his Integrative Medicine book, Rakel (Rakel, 2018) points to traditional whole-foods diets, and the Mediterranean diet is superior to a Western-style diet. The Western diet provides energy that is depleted of nutrients for the most part. In contrast, whole foods eating patterns provide folate, B vitamins, fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and monounsaturated fatty acids. All of these nutrients are important to good health and especially, brain health.
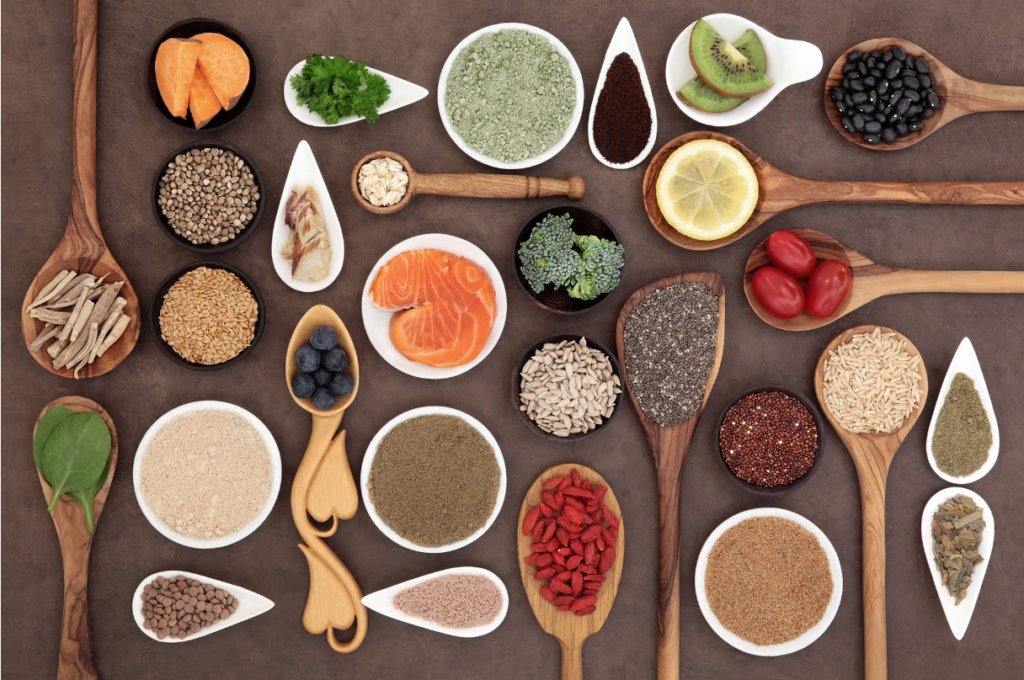

Did you know that when selecting an omega-3 supplement, it’s better to choose: omega-3 supplements containing 60% or more EPA, with a ceiling of 2,000 mg of EPA over DHA appears to be most effective. That was stated in a meta-analysis published in 2011. Sublette M, Ellis S, Geant A, Mann J. Meta-analysis of the effects of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in clinical trials in depression, J Clin Psychiatry 72(12):1577–1584, 2011.



Rakel also points out that eating three servings per week of small fish such as mackerel, herrings, wild Salmon, and sardines provides good content of omega-3. However, there is always the problem of heavy metal contamination and pesticide contamination. If possible, farmed fish is to be avoided due to toxin content (mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls).
It’s important to remember that docosahexaenoic acid is essential for the brain’s structural function and the retina. Eicosapentaenoic acid is responsible for communication across cell membranes.
References:
Depression. (n.d.). Retrieved May 7, 2022, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
Rakel, D. (2018). Integrative medicine.
Recent posts
-

Cholesterol and HbA1c Management in Premenopausal Women: What You Need to Know
07/09/2025 at 07:41
-

Brain Health and Nutrition: Boosting Cognitive Function and Immune Support Through Food
06/25/2025 at 12:18
-

Understanding Menopause and Perimenopause: Key Insights for Women’s Health
06/20/2025 at 13:23
-

Metabolic Health and Weight Loss: Unlocking the Key to Long-Term Success
06/20/2025 at 13:15
-

Antioxidants
06/14/2025 at 10:34
-
Anxiety and the gut: what is the relationship?
06/08/2025 at 13:42
-

The Power of Antioxidants
06/08/2025 at 13:31
-

Understanding Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Causes, Symptoms, and Nutritional Strategies
06/04/2025 at 09:38


Leave a reply